Product Details
Product Sizes
| Size | List Price | Price | Cart |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100 ul | $325.00 | Add to Cart |
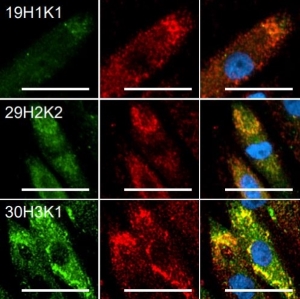
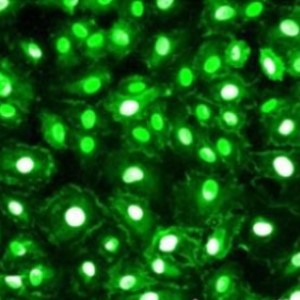
Parvalbumin is a cytoplasmic low molecular weight Ca2+ binding proteins with. It is the prototypic member of the very large family of proteins containing the "EF hand" Ca2+ binding motif. The nomenclature comes from the parvalbumin structure in which the fifth and sixth alpha helices, the E and F helices, form a V shape including acid amino acids which co-ordinate a single Ca2+. It turns out that close variants of this structure are found in many other Ca2+ binding proteins. Parvalbumin is expressed in fast-contracting muscles, where its levels are highest, as well as in the brain and some endocrine tissues. In brain, it is particularly concentrated in Purkinje cells and interneurons in the molecular layer of the cerebellum, but is also found in many GABAergic interneurons in the cortex. These GABAergic interneurons in most cases express only one of three Ca2+ binding proteins, namely parvalbumin, calretinin, or calbindin. As a result, these important inhibitory interneurons can be identified and subclassified based on their content of these three proteins. Each type of neuron as defined in this fashion has particular electrophysiological and functional properties. For example, calbindin positive interneurons are not fast-spiking as are parvalbumin expressing interneurons. Parvalbumin contains 3 EF-hand domains, domain AB, CD and EF. The N-terminal EF-hand of parvalbumin does not bind Ca2+, so that functional Ca2+ binding is between helices C and D and between helices E and F. The function of parvalbumin appears to be primarily buffering the Ca2+ level in cells. The absence of parvalbumin and calbindin disrupts the regulation of Purkinje cell firing rate and rhythmicity in vivo and parvalbumin dysfunction in cells critically contributes to abnormalities in oscillatory rhythms and network. The HGNC name for this protein is PVALB. |
Images
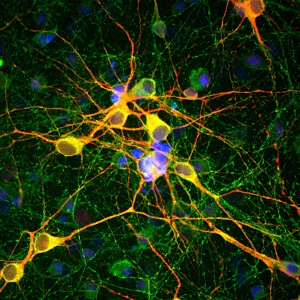
Adult rat cerebellum floating section was stained with MO22149 at 1:1,000 to parvalbumin in green. Parvalbumin is prominently expressed in the dendrites and perikarya of Purkinje cells and some interneurons in the molecular layer. Blue is a DNA stain.