Our human endothelial cells are constantly being used by researchers in their publications. This past month, both our human Retinal Microvascular Endothelial Cells (hRMECs) (cat # HEC09) and our human Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells (hBMECs) (cat # HEC02) were used in publications we'd like to highlight. You can find all customer publications using our endothelial cells here.
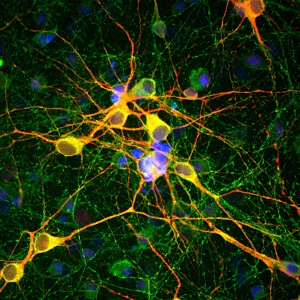
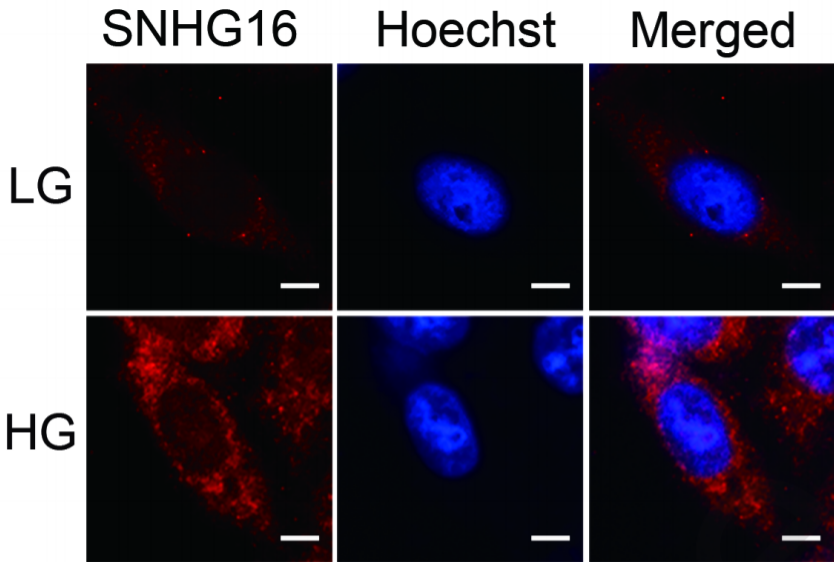
Image: SNHG16 subcellular distribution in hRMECs under low-glucose or high-glucose conditions.
In the first publication, investigators from Huazhong University of Science and Technology used our hRMECs in their diabetes research. Diabetic retinopathy has been shown to result from abnormal proliferation, migration, and angiogenesis of hRMECs in the retina. The researchers explored the role of long non-coding RNA small nucleolar RNA host gene 16 (SNHG16) in regulating hRMECs supplied by Neuromics in high-glucose conditions. After finding that SNHG16 likely plays a role in hRMEC dysfunction, they suggest their finding could provide a framework for diabetic retinopathy treatments.
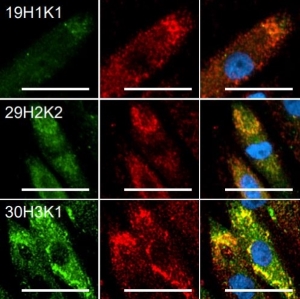
In the second publication, using Neuromics’ hBMECs, researchers from the Albert Einstein College of Medicine wanted to find a microRNA capable of targeting Neuropilin-1, a transmembrane glycoprotein. Recent studies have suggested that Neuropilin-1 plays an important role in the cellular entry of the SARs-CoV-2 virus, in addition to its known roles in angiogenesis, cancer, and immunity. The researchers chose to use our hBMECs because of their suitability for use in a blood-brain barrier model. They discovered that miR-24 is a functional modulator of Neuropilin-1 in hBMECs. Their finding could potentially be used for future research exploring COVID-19 and its relationship with Neuropilin-1 in endothelial cells.
In addition to our hRMECs and hBMECs, we have many endothelial cells available for countless types of research. You can explore all of our endothelial cells here.
Citations:
- Fei Cai, Huanzong Jiang, Yan Li, Qin Li, and Chao Yang. (2021). Up-Regulation of Long Non-Coding RNA SNHG16 Promotes Diabetes-Related Retinal Microvascular Endothelial Cell Dysfunction via Activating NF-κB and PI3K/AKT Pathways.Molecular Therapy: Nucleic Acid. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2021.01.035
- Pasquale Mone, Jessica Gambardella, Xujun Wang, Stanislovas S. Jankauskas, Alessandro Matarese, and Gaetano Santulli. (2021). miR-24 Targets the Transmembrane Glycoprotein Neuropilin-1 in Human Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells.Non-coding RNA, 7, 9. doi: 10.3390/ncrna7010009