Product Details
Product Sizes
| Size | List Price | Price | Cart |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100ul | $303.00 | Add to Cart |
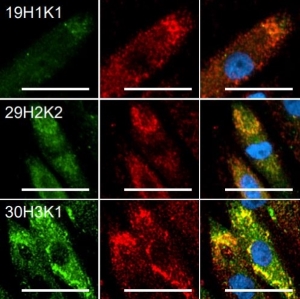
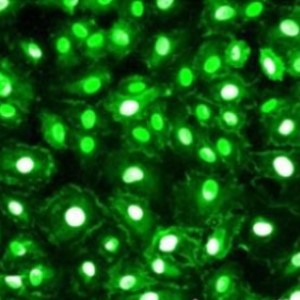
α-internexin is a Class IV intermediate filament protein originally discovered by two different groups of researchers as it copurifies with NF-L, NF-M and NF-H, the then better known major neurofilament “triplet” subunits. It is expressed only in neurons and in large amounts early in neuronal development, but is down-regulated in many neurons as development proceeds. Some neurons express α-internexin in the absence of NF-L, NF-M and NF-H, though most mature neurons express all four proteins. This α-internexin antibody has been shown, in peer reviewed publications, to reveal the upregulation of α-internexin in facial neurons following experimental axotomy followed by down regulation on axonal regeneration. It is also the standard reagent used to identify and classify patients with neurofilament inclusion body disease, a specific form of frontotemporal lobar dementia. Finally, it has been used to confirm the presence of circulating antibodies to α-internexin in the blood of certain patients with endocrine autoimmunity. |
Images
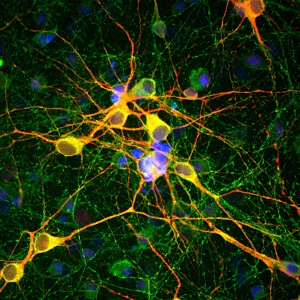
Immunohistochemistry of a section of rat facial nucleus 7 days following axotomy. These neurons are capable of regenerating their axons and also, concomitant with regeneration, strongly upregulate α-internexin in their perikarya. Other central neurons which are not able to regenerate their axons do not upregulate this protein after axotomy and untreated facial neurons normally show only very low levels of α-internexin. Both findings suggest that α-internexin has a role in axonal regeneration.
Western blot analysis of different tissue lysates using mouse mAb to α-internexin dilution 1:10,000 in red: [1] protein standard, [2] rat brain, [3] rat spinal cord, [4] mouse brain, [5] mouse spinal cord, and [6] cow spinal cord lysate. The MO22102 antibody reveals the α-internexin protein with an apparent molecular weight of 64-66kDa, with some variability across species.