Product Details
Product Sizes
| Size | List Price | Price | Cart |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100 ug | $325.00 | Add to Cart |
Secretagogin is a member of the EF-hand superfamily of Calcium-binding proteins. It was first cloned from pancreatic islets of Langerhans and neuroendocrine cells and is highly expressed in these tissues (1). Secretagogin is also expressed in numerous brain regions, although the expression pattern is not well conserved from rodents to humans (2,3). While human brain reveals an expression maximum in the cerebellum, in rat and mouse brain by far the highest expression is found in the olfactory bulb. Secretagogin has been shown to be involved in insulin secretion from pancreatic beta cells and is a strong candidate as a biomarker for endocrine tumors (4), and might be a useful biomarker for neuronal damage, stroke, and eventually psychiatric conditions (2,5-7). Moreover, secretagogin has been hypothesized to exert a neuroprotective role in neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s disease (8). |
Images
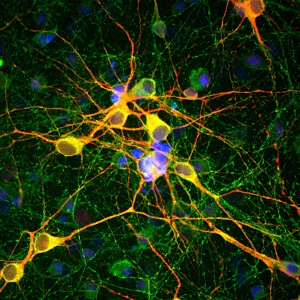
Immunofluorescent analysis of mouse brain olfactory bulb section stained with chicken pAb to secretagogin, CH22121, dilution 1:1,000, in red, and costained with mouse mAb to calretinin, dilution 1:500 in green. The blue is Hoechst staining of nuclear DNA.
Western blot analysis of tissue lysates using chicken pAb to secretagogin, CH22121, dilution 1:1,000 in green: [1] protein standard, [2] mouse olfactory bulb [3] rat cerebellum, and [4] cow cerebellum. The band at ~27kDa corresponds to the secretagogin protein. Secretagogin protein is highly expressed in the mouse olfactory bulb, but significantly less in the cerebellum.