Product Details
Product Sizes
| Size | List Price | Price | Cart |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100 ul | $303.00 | Add to Cart |
β-synuclein is a member of the synuclein protein family, the other two members being α and γ-synuclein, each protein being coded for by a distinct but related gene. α-synuclein was originally isolated as a major synaptic vesicle associated protein from the electric organ of the fish Torpedo, and direct homologues of α-synuclein are found in all vertebrates. Later work connected α-synuclein expression with several human brain pathologies, so that it is a major component of the Lewy bodies of Parkinson’s disease. β-synuclein was isolated as a component of normal and diseased human brain as a protein clearly related to but distinct from α-synuclein. The human β-synuclein molecule is 134 amino acids in size compared to 140 amino acids for α-synuclein, and the N-terminal halves of the two molecules are virtually identical while the C-terminal regions is more variable. |
Images
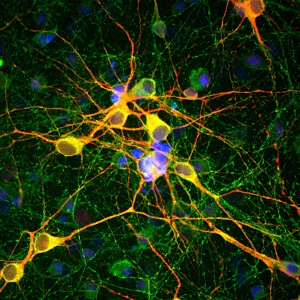
Immunofluorescent analysis of rat cerebellum section stained with rabbit pAb to β-synuclein dilution 1:1,000 in red, and costained with chicken pAb to parvalbumin dilution 1:5,000 in green. The blue is Hoechst staining of nuclear DNA. The β-synuclein antibody detects protein concentrated in synaptic regions, and parvalbumin antibody labels the perikarya and dendrites of Purkinje cells, and interneurons in the molecular layer of the cerebellum.
Western blot analysis of different tissue lysates using rabbit pAb to β-synuclein, RA22141, dilution 1:1,000 in green: [1] protein standard (red), [2] mouse cerebellum [3] mouse hippocampus, [4] rat cerebellum, [5] rat hippocampus, and [6] cow cerebellum. Strong band at about 17kDa corresponds to the β-synuclein protein.