Product Details
Product Sizes
| Size | List Price | Price | Cart |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100 ul | $303.00 | Add to Cart |
The CKI family consists of several different genes, divided in alpha, beta, gamma, delta and epsilon, some of which are encoded by more than one gene. The single mammalian CK1 alpha gene can generate four different proteins by alterate transcription. CK1a was raised against the shortest of these proteins, and will therefore bind to all CK1 isotypes. The CK1 alpha proteins are involved in the control of protein degradation, and phosphorylate acidic regions of their substrate molecules. Typically the target ser/thr residues closely C-terminal to two or three aspartic or glutamic acid residues. Alternately, phosphorylation on residues 3 or 4 amino acids N-terminal to a ser/thr residue can also favor CKI phosphorylation. This means that CKI family enzymes often phosphorylate one or more ser/thr residues C-terminal to a phosphorylation site generated by the activity of another protein kinase. CK1 alpha is plays a role in Alzheimer's and Sporadic Inclusion Body Myositis. Expression of the gene leads to accumulation of tau phospho-epitopes in both diseases. It is also suspected to be an apoptosis suppressor by binding to MDM2 and down regulating p53. |
Images
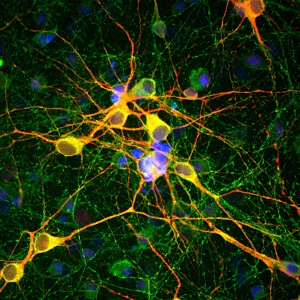
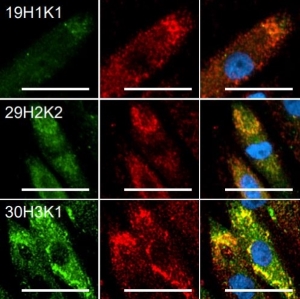
HeLa cells stained with chicken casein kinase 1 alpha antibody (red) and our panspecific mouse monoclonal antibody to nuclear pore complexes 39C7-a Panspecific Nuclear Pore Complex Marker. Casein kinase 1 alpha has a particulate distribution both in the nucleus and the cytoplasm. Blue is the Hoeschst DNA stain