Product Details
Product Sizes
| Size | List Price | Price | Cart |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100 ul | $325.00 | Add to Cart |
Calretinin is a member of the large superfamily of cytoplasmic Ca2+ binding proteins, thus belongs to the subclass of these containing the "EF hand" Ca2+ binding motif originally characterized in parvalbumin. Calretinin is expressed in mammalian central nerve system, testis, fallopian tube and pancreas. In the brain it is localized in certain classes of neurons, and antibodies to it are useful for identifying specific neuronal cell types. It is particularly concentrated in some cerebellar granular cells and their parallel fibers, but is also found in many GABAergic interneurons in the cortex. These GABAergic interneurons, in most cases, express only one of three Ca2+ binding proteins, namely calretinin, calbindin or parvalbumin . As a result, these important inhibitory interneurons can be identified and subclassified based on their content of these three proteins. Each type of neuron as defined in this fashion has particular electrophysiological and functional properties. For example, calbindin positive interneurons are not fast-spiking as are parvalbumin expressinginterneurons. Human calretinin is also known as 29 kDa calbindin and calbindin-2, for its sequence is related to calbindin. Calretinin contains six EF-hand domains. Four of them bind Ca2+ with high affinity in a cooperative manner, one with low affinity and the last one is non-functional, without Ca2+-binding ability. The function of calretinin appears to be primarily buffering the Ca2+ level in cells and affect intracellular calcium signals. Calretinin deficiency in mossy cells of the dentate gyrus and granule cells results in abnormal excitability in the cerebellar neuronal network and impairment of long-term potentiation and motor coordination. The HGNC name for this protein is CALB2. This antibody was raised against human calretinin protein expressed in and purified from E.coli. This antibody does not cross-react with the related calcium binding proteins calbindin and parvalbumin (see Blot image). |
- Product Reviews- - Rating:
Leave a review for this product and you could be eligible for a $10 Starbucks gift card.
- Product Publications
Product Publications
- Tyler Joseph Kramer. (2024). Exploring HOMER1 as a Postsynaptic Marker for Ribbon Synapses in the Peripheral Vestibular Epithelia. University of California Los Angeles, Master of Science Dissertation.
- Johnny A. Kenton, Tiahna Ontiveros, Clark W. Bird, C. Fernando Valenzuela, and Jonathan L. Brigman. (2020). Moderate Prenatal Alcohol Exposure Alters the Number and Function of GABAergic Interneurons in the Murine Orbitofrontal Cortex. Alcohol. doi: 10.1016/j.alcohol.2020.06.001
If you've used this product in a publication, let us know. Email pshuster@neuromics.com, with the publication details and you could be eligible for an Amazon gift card.
- Related Products
Related Products
Name Catalog # Size Bradykinin Receptor B2 RA14137 100 ul CADM1/SynCAM RA25084 100 ul Calbindin CH22118 100 ul Calbindin MO20016 100 ug Calreticulin MO22164 100 ul Calretinin MO20024 100 ul Calretinin MO22166 100 ul Calretinin RA22144 100 ul Calretinin (IgG1) MO22165 100 ul CaMKII2A GT41019 100 ug EpCAM (Epithelial Cell Adhesion Molecule)/Epithelial Specific Antigen MO47063 100 ul MARCKS (Myristoylated Alanine Rich C Kinase Substrate) CH22137 100 ul MARCKS (Myristoylated Alanine Rich C Kinase Substrate) RA22111 100 ul Neurogranin precursor GT41024 100 ug phospho-Synapsin (Ser9) RA18009 100 ul S-100 MO47059 100 ul SHANK1a N-Terminus RA19015 100 ug Striatin RA25067 100 ul Synapsin RA18010 100 ul
Images
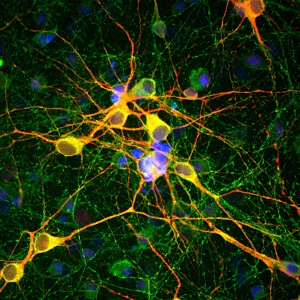
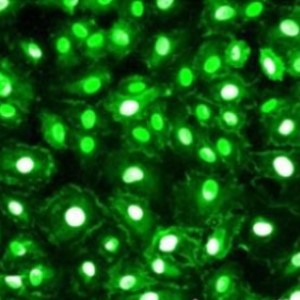
Adult rat brain hippocampus section (45 μM; fixed by transcardial perfusion with 4% paraformaldehyde) was stained with CH22116 (1:1,000, red), and our rabbit anti-MeCP2 (RA22123 green). Calretinin labels a subset of hippocampal interneurons, which also express MeCP2 in the nucleus to give a yellow color
Adult rat brain hippocampus section (45 μM; fixed by transcardial perfusion with 4% paraformaldehyde) was stained with CH22116 (1:1,000, red), and our rabbit anti-MeCP2 (RA22123 green). Calretinin labels a subset of hippocampal interneurons, which also express MeCP2 in the nucleus to give a yellow color
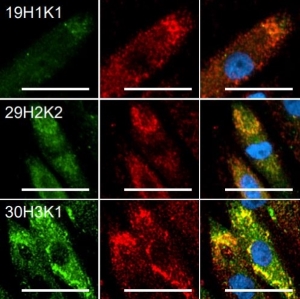
Adult rat cortex section was co-stained with Calretinin (CH22116; red) and our mouse anti-calbindin antibody (MO22146; green). Each antibody specifically labels a subset of interneurons (i.e., calretinin-positive or calbindin-postive) that express each marker exclusively. Insets are high-magnification images of the boxed area in each picture. Blue is Dapi staining that labels DNA.
Adult rat cortex section was co-stained with Calretinin (CH22116; red) and our mouse anti-calbindin antibody (MO22146; green). Each antibody specifically labels a subset of interneurons (i.e., calretinin-positive or calbindin-postive) that express each marker exclusively. Insets are high-magnification images of the boxed area in each picture. Blue is Dapi staining that labels DNA.